- 400IT Networking Coursework 1 Practical Assessment – Lab Scenario Worksheet
- MAR001-1 Principles of Marketing Assignment Brief 2026 | University of Bedfordshire
- MAR0022-1 Consumer Behaviour Assignment 1 Brief 2026 | University of Bedfordshire
- BTM4FUB Fundamentals of Business Finance Assignment 2 Brief 2026 | CCCU
- OTHM Level 6 Diploma In Health And Social Care Management Assignment Brief 2026
- PBS7000J Capstone Project Final Assessment 2026 | University of Plymouth
- ILM Unit (8600–308) Understanding leadership Assignment Brief 2026
- PSY771 Research Project Assignment Brief 2026 | Wrexham University
- CIH Level 3 H3007 Involving Housing Service Users Assignment Brief 2026
- BTEC Level 3 Unit 11 Psychological Perspectives Assignment Brief 2026
- HSC 4001 Epidemiology and Health Science Assessment Brief 2026 | BNU
- CSE4202 Fundamentals in Programming Assessment Brief 2026 | CMU
- BS7014 International Business Strategy Assignment Brief 2026 | KU London
- BUS4014 People Management Assignment Plans and Structures- Plan 2026 | Arden University
- BUS4013 Technology and Innovation Assignment Plans and Structures- Plan 2026 | Arden University
- CSY3062 Cyber Security and Applied Cryptography Assessment Brief 2026
- COM4006 Introduction to Academic Skills and Professional Development Assessment Brief 2026
- DSM030 Statistics and Statistical Data Mining Assignment Brief 2026 | UOL
- Unit 5 Understand the Role of the Social Care Worker Assessment Question 2026
- Leading and Managing Change Assessment 1 2026 | University of Greenwich
Unit 5011 Industrial Power Electronics and Storage Pearson BTEC Level 5 Assignment Brief
| University | University Centre Leeds (UCL) |
| Subject | Unit 5011 Industrial Power Electronics and Storage |
Leeds City College Higher Education
Pearson BTEC Level 5 Higher National Certificate in Electrical and Electronic Engineering for England

2025-2026
Do You Need Assignment of This Question
INTRODUCTION
This unit presents a wide-ranging introduction to the field of existing and renewable energy systems. There are many alternative sources of energy (some ‘green’) which can be converted to an electrical form, providing energy for transport, heat/cooling and lighting, as well as energy for various industrial processes and applications.
Power electronic converters are an essential component of renewable and distributed energy sources, including wind turbines, photovoltaics, marine energy systems and energy storage systems. It is necessary to gain a clear understanding of, and be able to examine, the technical implications of providing sustainable electrical energy to meet the energy demand of the future.
The unit will also explore the potential impacts of climate change and why more, and different forms of, sustainable energy sources are required together with the need for energy efficiency measures.
By the end of this unit students will be able to examine the technological concepts behind providing a sustainable electrical energy supply for the future. They will also be able to describe how the fundamental technical and economic processes and drivers at play in the electrical power industry affect the selection and use of energy sources.
DELIVERY
The main mode of delivery of this 30 hours module is lectures supported by classroom discussions and student presentations. The material discussed during class will be available on Google Classroom for self-study and will be complemented by preparatory learning material.
Students are expected to attend all teaching sessions and to submit work on time. It is expected that students should allocate approximately 150 study hours per module (for a 15 credit module). This will include lectures and tutorials, VLE based activities, research and assessment preparation and submission.
If for some reason you are unable to attend then you must inform your module tutor. In cases of illness you should also provide a doctor’s note.
You are expected to meet submission deadlines detailed in this handbook. For information on the penalties for late/non submission please see the Academic Regulations which can be found on the VLE.
TUTOR
Dr Md Akmol Hussain is the Programme Manager for Engineering at University Centre Leeds. He holds a teaching qualification (PGCE) with Qualified Teacher Status, as well as over 10 years of experience teaching a wide range of engineering courses – including Electrical/Electronics, Robotics, Engineering Maths and PLCs – at various levels, from Level 3 to degree. He also holds a PhD in Computer Vision, a Postgraduate Certificate (research-based), a B.Eng in Electronics and Communication Engineering, and an HND in Electrical and Electronics Engineering, providing him with a solid academic and practical foundation.
Dr Hussain has published 4 high impact journal articles in IEEE Access, 6 conference papers, and a book chapter. His research focuses on digital image and video processing, and control engineering, particularly the design and implementation of automated systems through programming and algorithm development.
MODULE SPECIFICATION
LO1 Evaluate the energy demand to determine the technology and methods of energy production
Energy demand:
- Historical energy production, energy consumption, environmental aspects and
- global warming.
- The need for energy systems and global energy demand over the short to long term.
- Environmental effects associated with energy generation and consumption.
- Practicality, benefits, drawbacks, and effectiveness of renewable energy sources.
- Overview of non-renewable and renewable energy technologies (wind, solar, bio, hydro, geothermal) and the associated costs.
- Future energy trends, scenarios, and sustainable energy sources.
LO2 Explore current energy efficiency measures, technologies, and policies specific to the building and transportation sectors
Energy auditing, management, costs, requirements, bench marking and optimisation:
- Energy management, planning, monitoring, policy, ecology, and environment.
Energy and buildings:
- Overview of the significance of energy use and energy processes
- Internal and external factors on energy use and the attributes of the factors
- Sustainable buildings, Status of energy use in buildings and estimation of energy use in a building.
- Standards for thermal performance of building envelope and evaluation of the overall thermal transfer.
- Measures and technologies to improve energy efficiency in buildings, SWOT analysis.
Energy and electric vehicles:
- Electrical vehicle configurations, requirements, and circuit topology; full electric and plug in hybrid vehicles
- Policies, charging infrastructure, grid implications, measures, and technologies to support more sustainable transportation, SWOT analysis
- Use of MATLAB/Simulink or alternative appropriate software to model, simulate and analyse the energy efficiency of a typical standard house or electric vehicle.
LO3 Analyse the control techniques of power electronics for renewable energy Systems
Control techniques:
- Environmental aspects of electrical energy conversion using power electronics
- Introduce design criteria of power converters for renewable energy applications
- Analyse and comprehend the various operating modes of wind electrical generators and solar energy systems
- Introduce the industrial application of power converters, namely AC to DC, DC to DC and AC to AC converters for renewable energy systems
- Explain the recent advancements in power systems using the power electronic systems. Introduction to basic analysis and operation techniques on power electronic systems
- Functional analysis of power converters’ main topologies
- Use of MATLAB/Simulink to model, simulate and analyse the dynamic behaviour of a simple renewable energy system.
LO4 Investigate the impacts of renewable resources to the grid and the various issues associated with integrating such resources to the grid
Impact of renewable resources:
- Safe and secure operation of a simple power system
- Standalone and grid connected renewable energy systems
- Introduction to smart grid, features, functions, architectures, distributed generation, grid integration and implications. Grid interactive systems, grid tied systems, inverters, and application of its devices
- Smart homes, power management, smart grid, intelligent/smart metering
- Communication technologies and power electronics modules for smart grid network, importance of power electronics in smart grid, for example energy storage (electrical, chemical, biological, and heat), and the future of smart grid
- Use of MATLAB/Simulink to model, simulate and analyse the dynamic behaviour of a standard smart grid
- Discuss in groups popular and latest models of integrating a diverse range of renewable resources to the grid.
SCHEME OF WORK
| Week no. | w/c | Topic | Advance Reading | Deadlines |
| 1 | 15/09/2025 | Introduction LO1/Energy consumption | ||
| 2 | 22/09/2025 | LO1/Impact of energy consumption and generation | MacKay (2009) | |
| 3 | 29/09/2025 | LO1/Renewable sources | ||
| 4 | 06/10/2025 | LO2/Energy auditing, management, costs etc | Review: PES1 | |
| 5 | 13/10/2025 | LO2/Energy and buildings | ||
| 6 | 20/10/2025 | LO2/Energy and electric vehicles | MacKay (2009), pp 50ff, pp 140ff | Submission: PES1 |
| 27/10/2025 | Reading Week | MacKay (2009), pp 118ff | ||
| 7 | 03/11/2025 | LO1&LO2/Discussion of Matlab/Simulink | ||
| 8 | 10/11/2025 | LO3/Operating modes of wind and solar generators | ||
| 9 | 17/11/2025 | LO3/Power converter | Abu-Rub (2014), pp 788ff | |
| 10 | 24/11/2025 | LO3/ simulate simple renewable energy system with Matlab/ Simulink | Submission: PES1 | |
| 11 | 01/12/2025 | LO4/Smart grids
| ||
| 12 | 08/12/2025 | LO4/Interaction with grid | Review PES2 | |
| 13 | 15/12/2025 | LO4/Issues with grid interaction | Abu-Rub (2014), pp 191ff | |
| 22/12/2025 | Christmas Holidays | |||
| 29/12/2025 | Christmas Holidays | |||
| 14 | 05/01/2026 | Review and module Evaluation | Submission: PES2 | |
| 15 | 12/01/2026 | Review and module Evaluation |
Reference:
MacKay, D J C. (2009). Sustainable Energy — without the hot air. Cambridge: UIT Cambridge Ltd
Abu-Rub, H. (2014). Power Electronics for Renewable Energy Systems, Transportation and Industrial Applications. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons
Buy Answer of This Assessment & Raise Your Grades
PES1: Energy Demand and How to Reduce It
| COURSE TITLE | Pearson BTEC Level 5 Higher National Certificate in Electrical and Electronic Engineering for England | ||
| MODULE TITLE | Unit 5011 – Industrial Power, Electronics and Storage | ||
| TITLE OF ASSIGNMENT | PES1: Energy demand and how to reduce it | ||
| DEADLINE DATE FOR SUBMISSION BY STUDENTS | |||
| SUBMISSION LOCATION | Turnitin | ||
| ASSESSOR(S) | |||
LEARNING OUTCOMES ASSESSEDLO1 Evaluate the energy demand to determine the technology and methods of energy production. LO2 Explore current energy efficiency measures, technologies, and policies specific to the building and transportation sectors. | |||
| NOTES FOR STUDENTS What is Academic Malpractice? Academic malpractice relates to academic work that does not meet normal standards of academic practice and encompasses all kinds of academic dishonesty, whether deliberate or unintentional, which infringes the integrity of the College’s assessment procedures. ‘Candidate malpractice’ means malpractice by a candidate in the course of any examination or assessment, including the preparation and authentication of any controlled assessments or coursework, the presentation of any practical work, the compilation of portfolios of assessment evidence and the writing of any examination paper. | |||
Learner declaration (authentication) |
| I certify that the work submitted for this assignment is my own and research sources are fully acknowledged.
Student signature: Date: |
For each submission: Fill in, sign and submit together with your assignment
Higher Nationals
Assignment Brief – BTEC (RQF)
Higher National Diploma in Engineering (Electrical and Electronic Engineering)
| Student Name /ID Number | |
| Unit Number and Title | Unit 5011 – Industrial Power, Electronics and Storage |
| Academic Year | 2025/26 |
| Unit Assessor | |
| Assignment Title | PES1: Energy demand and how to reduce it |
| Review Date | 10/11/25 |
| Submission Date | |
| IV Name | |
| Date |
Submission Format: |
| The submission is in the form of an individual written report. This should be written in a concise, formal business style using single spacing and font size 12. You are required to make use of headings, paragraphs and subsections, as appropriate, and all work must be supported with research and referenced using the Harvard referencing system. Provide a bibliography using the Harvard referencing system. The recommended word limit is 1500 – 2000 words. Note to students: ● To maximise your learning outcome attempt all tasks in this assignment regardless of what you have achieved in other assignments/units. (Any appeal against an assessment decision will apply to only the assignment in question and will not affect other assessment decisions.) ● Submit your assignment with a signed front sheet (for authentication) to TurnItIn. |
Unit Learning Outcomes: |
| LO1 Evaluate the energy demand to determine the technology and methods of energy production. LO2 Explore current energy efficiency measures, technologies, and policies specific to the building and transportation sectors. |
Assignment Brief and Guidance: |
SenarioAs an energy consultant you work with your clients to help them make the most of energy use, be that by helping them to reduce their costs, increase their use of green energy, or attain accreditations such as those awarded by the Carbon Trust for offsetting their energy use. One of your clients is interested in an overview of current renewable energy sources and how to save energy, therefore you have to report back in a formal report. Task 1In order to satisfy your clients queries you need to:
and write a technical report based on this research. In addition, you could report back on your assessment of the global impact on energy demand based on the energy sources you have used above. After that, you could evaluate the effectiveness and drawbacks of renewable energy systems for short and long term energy demands. Finally, a critical evaluation of the performance of a renewable energy system and the technologies used in energy efficiency improvement could be of interest to your client as well. Task 2In a separate part of your report you need to discuss current energy efficiency measures, determine the main factors that impact on energy use and efficiency in a building and discuss the technologies that could be used to support more sustainable transport. You could also illustrate how to apply modelling of energy management in a building or electric vehicle using Matlab/Simulink (or equivalent), such as building timers to control lighting levels in offices. This could be followed by an evaluation of the selection of suitable technologies to improve energy efficiency in a building or electric vehicle. As a last item you could analyse the dynamic performance of a power electronic converter for a given renewable energy source (such as a PV grid connected system[1]) and calculate the energy and cost savings against conventional power sources, including consideration for development and installation costs. |
Learning Outcomes and Assessment Criteria | |||
| Learning Outcome | Pass | Merit | Distinction |
| LO1 Evaluate the energy demand to determine the technology and methods of energy production
| P1: Evaluate the energy demand of a specific scenario or case study by identifying the required technology and methods of energy production with reasoning or consideration of alternatives.
| M1: Determine the effectiveness and drawbacks of renewable energy systems for short- and long-term impact on energy demands. | D1: Justify the most Suitable technologies and methods of energy production for the local area, backed by relevant data or research.
|
| LO2: Explore current energy efficiency measures, technologies, and policies specific to the building and transportation sectors | P2: Explore energy efficiency measures, technologies, and policies in the building and transportation sectors suggesting alternatives. | M3: Provide detailed SWOT analysis of various energy efficiency measures, technologies, and policies in the building and transportation sectors. | D2: Conduct an impact analysis of current and emerging energy efficiency measures, technologies and policies in the building and transportation sectors, with insightful recommendations or predictions for future developments. |
Are You Looking for Answer of This Assignment or Essay
PES2: Efficiency measures for building and transportation
| COURSE TITLE | Pearson BTEC Level 5 Higher National Certificate in Electrical and Electronic Engineering for England | ||
| MODULE TITLE | Unit 5011 – Industrial Power, Electronics and Storage | ||
| TITLE OF ASSIGNMENT | PES2: Efficiency measures for building and transportation | ||
| DEADLINE DATE FOR SUBMISSION BY STUDENTS | |||
| SUBMISSION LOCATION | Turnitin | ||
| ASSESSOR(S) | Md Akmol Hussain | ||
LEARNING OUTCOMES ASSESSEDLO3 Analyse the control techniques of power electronics for renewable energy systems LO4 Investigate the impacts of renewable resources to the grid and the various issues associated with integrating such resources to the grid | |||
NOTES FOR STUDENTSWhat is Academic Malpractice? Academic malpractice relates to academic work that does not meet normal standards of academic practice and encompasses all kinds of academic dishonesty, whether deliberate or unintentional, which infringes the integrity of the College’s assessment procedures. ‘Candidate malpractice’ means malpractice by a candidate in the course of any examination or assessment, including the preparation and authentication of any controlled assessments or coursework, the presentation of any practical work, the compilation of portfolios of assessment evidence and the writing of any examination paper | |||
Learner declaration (authentication) |
| I certify that the work submitted for this assignment is my own and research sources are fully acknowledged. Student signature: Date: |
For each submission: Fill in, sign and submit together with your assignment Higher Nationals
Assignment Brief – BTEC (RQF)
Higher National Diploma in Engineering (Electrical and Electronic Engineering)
| Student Name /ID Number | |
| Unit Number and Title | Unit 5011 – Industrial Power, Electronics and Storage |
| Academic Year | 2025/26 |
| Unit Assessor | |
| Assignment Title | PES2: Efficiency measures for building and transportation |
| Review Date | 2025 |
| Submission Date | |
| IV Name | |
| Date | 18/09/25 |
Submission Format: |
| The submission is in the form of an individual written report. This should be written in a concise, formal business style using single spacing and font size 12. You are required to make use of headings, paragraphs and subsections, as appropriate, and all work must be supported with research and referenced using the Harvard referencing system. Provide a bibliography using the Harvard referencing system. The recommended word limit is 1500 – 2000 words. You will not be penalised for exceeding the total word limit. Note to students: ● To maximise your learning outcome, attempt all tasks in this assignment regardless of what you have achieved in other assignments/units. (Any appeal against an assessment decision will apply to only the assignment in question and will not affect other assessment decisions.) ● Submit your assignment with a signed front sheet (for authentication) to TurnItIn. |
Unit Learning Outcomes: |
| LO3 Analyse the control techniques of power electronics for renewable energy systems LO4 Investigate the impacts of renewable resources to the grid and the various issues associated with integrating such resources to the grid |
Assignment Brief and Guidance: |
SenarioAs an energy consultant you work with your clients to help them make the most of energy use, be that by helping them to reduce their costs, increase their use of green energy, or attain accreditations such as those awarded by the Carbon Trust for offsetting their energy use. One of your clients is interested in how to control and integrate renewable energy sources so the mains have to report back in a formal report. Task 1In order to satisfy your clients queries you need to:
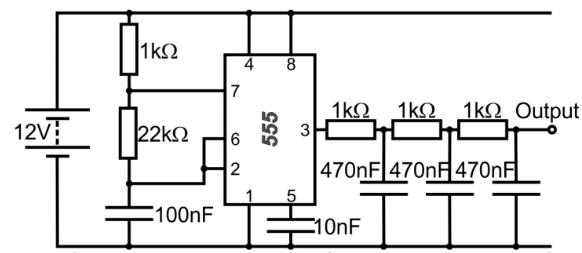
In addition, you could report back on your simulation of a simple power converter for a typical renewable energy system using a standard software package such as Matlab/Simulink (or equivalent) and critically analyse the use of the power converter selected above for a renewable energy application. To do this you could use the following case study. Voltage source inverters (VSI) are devices which convert direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). A single phase voltage source inverter consists of a DC voltage source (such as a battery, which may be used for energy storage in a renewable energy system, or solar cells), a DC link capacitor (which acts as an open circuit for dc current), 4 transistors (such as IGBT, BJT, MOSFET, GTO) for switching, and 4 antiparallel diodes ( which are used to allow non-unity power factor at output). The topology of a single phase VSI consists of two legs switches and two load terminals; each leg has upper and lower switches which are controlled by pulse width modulation (PWM) signals. (See, for instance, Gazis et al (2010)[2].) The circuit shown in Figure 1 is a model of such a single-phase voltage source inverter based on a 555 timer. Simulate this circuit in Multisim and observe its input voltage alongside its output voltage. Write a short report using the simulation screenshots to show how you have designed this inverter. Furthermore, critically analyse the use of VSI for a renewable energy application.
Figure 1: Model of a single phase voltage source inverter To improve your report further you could critically evaluate the dynamic performance of integrating renewable energy sources to the smart grid network using a standard industrial based software, such as MATLAB/Simulink software (or equivalent). Task 2In a separate part of your report, you need to:
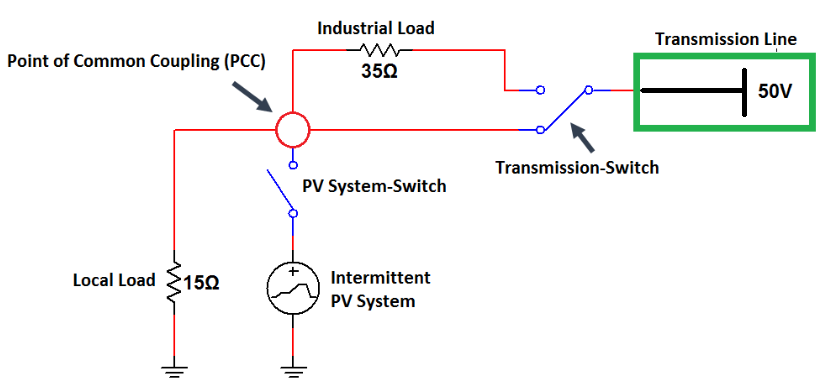
In an optional part of your report, you could analyse how power electronic converters are used in smart grid networks and evaluate the issues associated with integrating renewable energy sources to the grid. Finally, you could critically analyse the impact of renewable energy sources and their integration to the grid using standard industrial based software such as MATLAB/Simulink (or equivalent). In order to do this you could use the following simplified model of a PV system integrated to a transmission network in Figure 1. It consists of a piecewise linear voltage source which represents an intermittent PV system, a transmission line, an industrial and local load, a PV system and transmission switch, and point of common coupling (PCC) where all these are connected. You could simulate this circuit, using MultiSim, to analyse the impact of the PV system voltage at the PCC, and write a short report to critically analyse the impact of renewable energy sources and their integration to the grid.
Figure 1: Simplified model of a PV system integrated to a transmission network This model could be used to illustrate how networks or load switching can result in voltage sag on distribution lines and how Integrated renewable energy systems can provide real time power support to an existing network and help to stabilise the voltage profile in the distribution lines. |
Learning Outcomes and Assessment Criteria | |||
| Learning Outcome | Pass | Merit | Distinction |
| LO3: Analyse the control techniques of power electronics for renewable energy systems
| P3: Analyse the control techniques of power electronics for a given renewable energy system, applying understanding of the key concepts and practices.
| M3: Provides an analysis of the control techniques of power electronics for renewable energy systems, demonstrating a clear understanding of the theoretical principles and practical applications, including identification of strengths and weaknesses of various techniques. | D3: Conduct an in-depth impact analysis of the control techniques of power electronics for renewable energy systems, demonstrating a superior understanding of principles, applications and future trends.
|
| LO4: Investigate the impacts of renewable resources to the grid and the various issues associated with integrating such resources to the grid
| P4: Investigate key impacts of renewable resources on the grid and issues associated with integrating such resources | M7: Evaluate the impacts of renewable resources on the grid and the issues with integration, demonstrating an understanding of the complexities involved. | D4 Synthesise the challenges and potential solutions, drawing on relevant case studies and cutting-edge research.
|
Recommended Resources
Note: See HN Global for guidance on additional resources.
Print Resources
- Ackermann T. (2012) Wind Power in Power Systems. Wiley.
- Bhimbhra P.S. (2012) Power Electronics. Khanna Publishers.
- Cole B. (Editor) (2023) Power Electronics: Devices, Circuits and Applications (Hardback). Clanrye International.
- Duffie J.A. and Beckman W. A. (2013) Solar Engineering of Thermal Processes. Wiley.
- Dugan R.C., McGranaghan M.F., Santoso S., and Beaty H.W. (2012) Electrical Power
- Systems Quality, Third Edition (Electronics) Hardcover – Illustrated. McGraw Hill.
- Fekik A., Ghanes M. and Denoun H. (Editors) (2023) Power Electronics Converters and
- their Control for Renewable Energy Applications (Paperback). Elsevier Science & Technology.
- Kassakian J.G., Perreault D.J., Verghese G.C. and Schlecht M.F. (2023) Principles of Power Electronics (Hardback). Cambridge University Press.
- Kumar S., Singh B., and Singh A.K. (Editors) (2023) Recent Advances in Power Electronics and Drives: Select Proceedings of EPREC 2021 − Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering 852 (Paperback). Springer.
- Kumar N., Guerrero J.M., Kastha D., and Saha T.K. (Editors) (2022) Power Electronics for Next-Generation Drives and Energy Systems. Volume 1: Converters and control for drives. IET Digital Library.
- Masters G.M. (2013) Renewable and Efficient Electric Power Systems (IEEE Press) Hardcover – Illustrated. Wiley-IEEE Press.
- Na (2014) A Course in Electrical and Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation (Nineteenth Revised Edition 2011 Reprint 2014) Paperback. NA.
- Peake S. (Editor) (2017) Renewable Energy: Power for a Sustainable Future Paperback – Illustrated. OUP Oxford.
- Rashid M.H.(Editor) (2023) Power Electronics Handbook (Hardback). Elsevier.
- Vittal V., Mccalley J.D., Anderson P.M., and Fouad A.A. (2019) Power System Control and
- Stability (IEEE Press Series on Power and Energy Systems) Hardcover. Wiley-IEEE Press.
- Willis H.L. (Editor) (2018) Distributed Power Generation: Planning and Evaluation. eBook. Routledge.
Journals
Note: Example journals listed below provide a broad range of articles related to unit content and
those relevant for the qualification. Staff and students are encouraged to explore these journals
and any other suitable journals to support the development of academic study skills, and subject
specific knowledge and skills as part of unit level delivery.
- Energies
- Energy and Buildings
- Energy Policy
- IEEE Power and Energy Magazine
- IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics
- International Journal of Electrical Power and Energy Systems
- International Journal of Sustainable Transportation
- Journal of Cleaner Production
- Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews
- Renewable Energy
- Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment
[1] See, for instance: Kjaer, S B. 2005. A Review of Single-Phase Grid-Connected Inverters for Photovoltaic Modules. IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRY APPLICATIONS
[2] Gazis, P., Vokas, G.Α. and Papathanasiou, S., 2010, September. Trends of power electronics on renewable energy systems. In Proc. Int. Sci. Conf. e RA–5, Piraeus, Greece.
Do You Need Assignment of This Question
Working on your Industrial Power Electronics and Storage Assignment and finding it tough to explain converters, inverters, or energy storage systems? Don’t stress — our team of engineering experts can guide you step by step. We help you write clear, well-researched answers that meet your Pearson Level 5 standards. Each paper is 100% plagiarism-free, AI-free, and tailored to your coursework needs. Get Students Assignment Help support you need today and make your assignment stand out with confidence.